Jaws (Orthognathic & TMJ)
Balanced jaws support function, airway and facial harmony. This section brings together surgical and non-surgical solutions—from double jaw surgery for bite and airway correction to genioplasty, salivary gland surgery, and comprehensive care for TMJ disorders & clenching.
What we address
- Class II/III malocclusion, open bite, deep bite, facial asymmetry
- Airway-driven indications (selected obstructive sleep apnoea candidates)
- Gummy smile from vertical maxillary excess; weak or prominent chin
- TMJ pain, clicking, locking, clenching/bruxism
- Salivary gland problems: stones (sialolithiasis), recurrent infections, benign tumours (parotid/submandibular)
Treatment categories
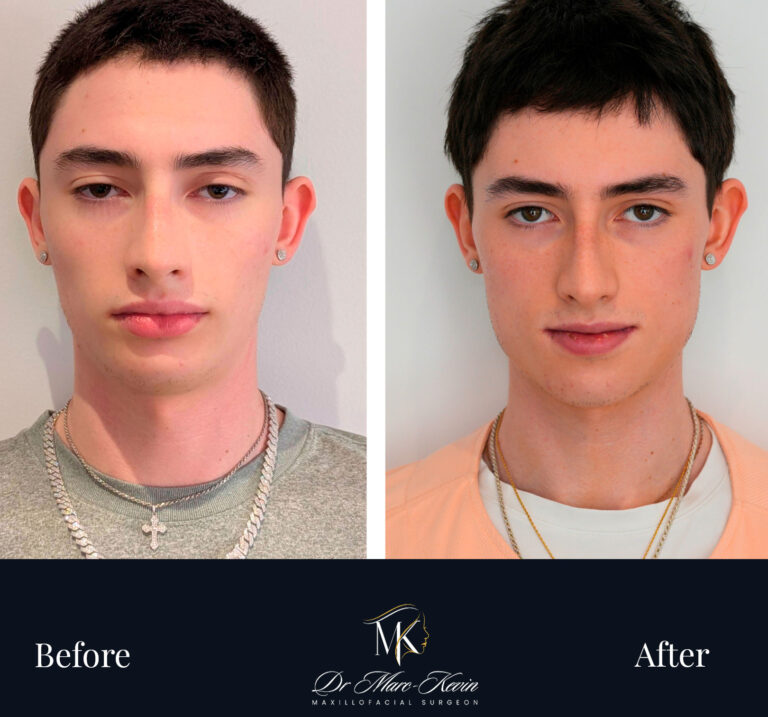
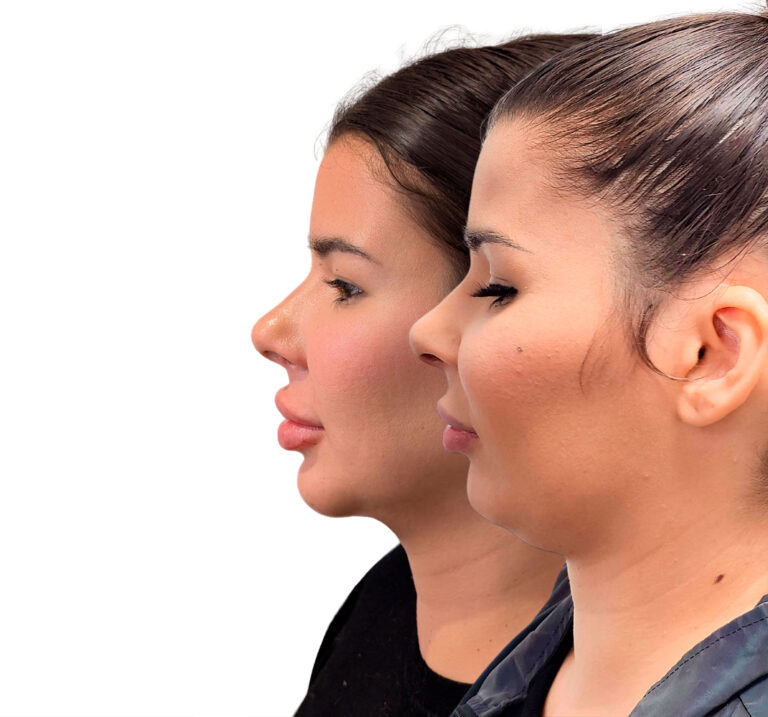
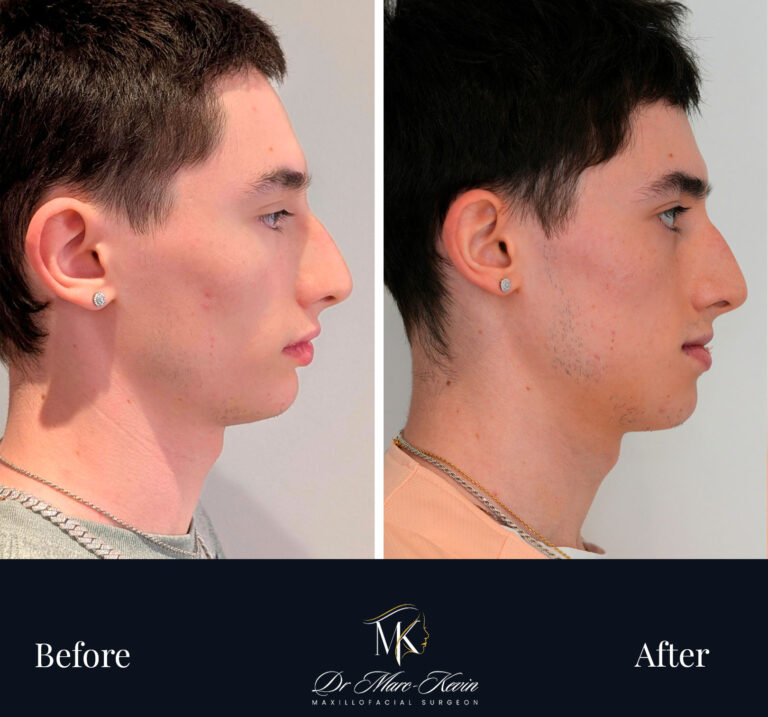
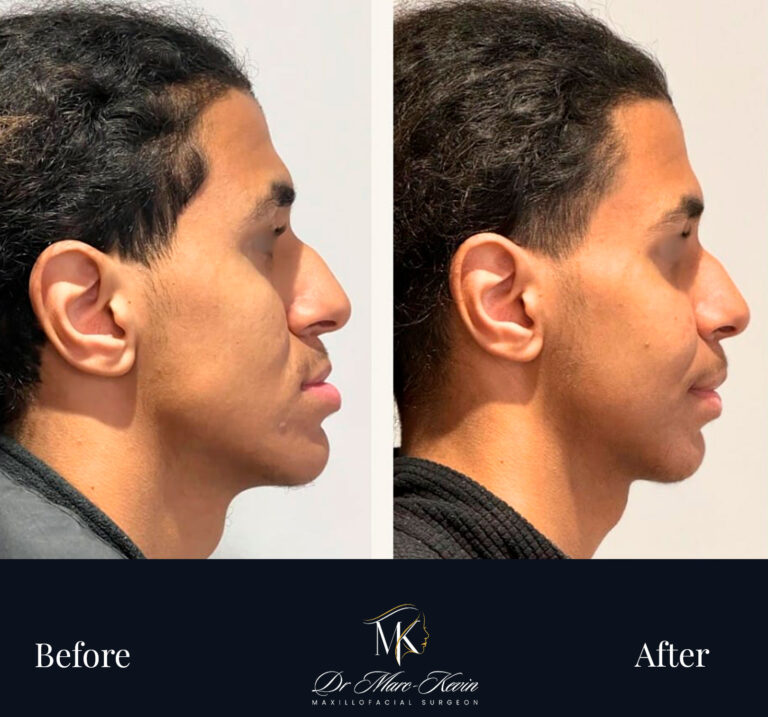
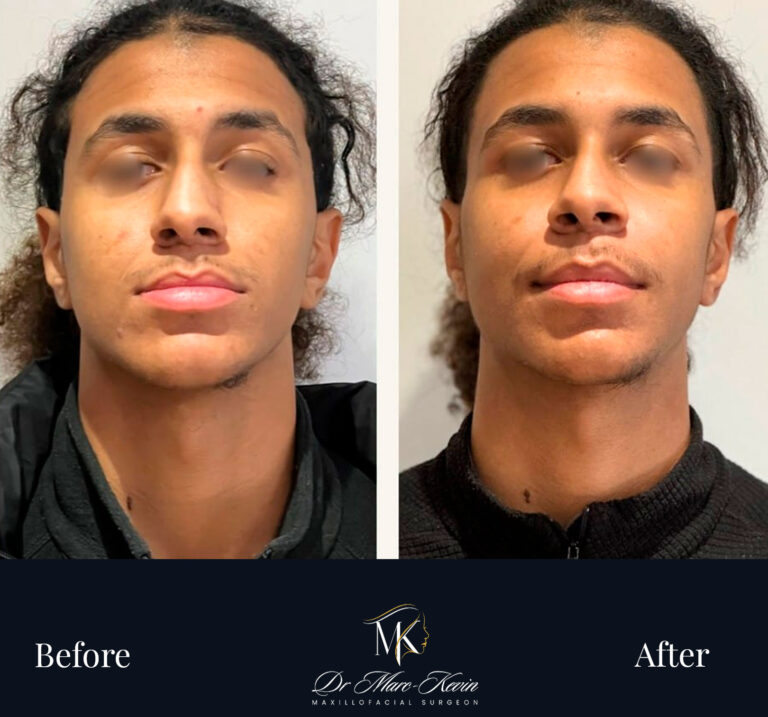
Double Jaw Surgery (Orthognathic)
Bimaxillary surgery repositions the maxilla and/or the mandible to correct bite, improve facial balance and—in selected cases—expand the airway. Planned with 3D simulation and splints/guides for accuracy; delivered in coordination with your orthodontist.
Genioplasty (Chin Surgery)
Precise osseous chin repositioning (advance, set-back, lengthen/shorten, centre) via an internal approach—no external scars. Improves profile harmony and lip competence; can be combined with jaw surgery or performed alone.
Salivary Glands Surgery
Minimally invasive sialendoscopy for stones and strictures when possible; targeted open surgery (parotid/submandibular) when required with nerve-sparing technique and discreet incisions. Specimens sent for histology; coordinated imaging and follow-up.
TMJ Disorders & Clenching
Structured pathway: diagnosis → conservative care (splints, physio, medication), injectables when appropriate (e.g., masseter modulation), and arthrocentesis/arthroscopy for mechanical issues. Open TMJ surgery reserved for clear structural pathology.
Non-surgical vs surgical — choosing wisely
- Conservative first for TMJ/clenching: bite appliances, physiotherapy, behaviour & sleep hygiene, targeted medication; consider masseter neuromodulation (botox, jawtox) when muscle overactivity dominates.
- Surgical when structure is the driver: skeletal discrepancies, airway collapse candidates, persistent mechanical TMJ pathology, or salivary stones/tumours not suited to endoscopic care.
I recommend the least invasive option that will genuinely meet your goals and remain stable.
Typical timelines & downtime (indicative)
- Double Jaw Surgery: 1–2 nights in hospital; swelling peaks days 2–3; soft diet 2–4 weeks; return to desk work ~2–3 weeks; bone consolidation 6–8 weeks (full sport later).
- Genioplasty: day case or 1 night; soft diet ~1 week; most desk work 7–10 days.
- Salivary (sialendoscopy): same-day in most cases; mild swelling 24–72 h.
- Parotid/Submandibular open surgery: usually 1 night; drain ~24 h; careful scar and nerve monitoring.
- TMJ arthrocentesis/arthroscopy: day case; soreness 24–72 h with post-op physio.
Safety & transparency
- 3D virtual planning and splints/guides for orthognathic accuracy
- Nerve-aware surgery: inferior alveolar/mental nerve (mandible), facial nerve branches (parotid)
- Airway & orthodontic coordination to protect long-term stability
- Clear consent on risks: bleeding, infection, nerve sensation changes (often temporary), relapse/asymmetry, joint symptoms, salivary leak/Frey’s (parotid), need for staged procedures
- Routine histopathology for salivary specimens
FAQs
Will my face change after double jaw surgery?
Yes—by design. Repositioning the jaws improves proportions, smile and airway.
Are jaws wired shut?
Rigid fixation with plates/screws usually allows early movement and soft diet—no prolonged wiring in most modern cases.
Can jaw surgery help sleep apnoea?
In selected patients, maxillo-mandibular advancement can enlarge the airway. We coordinate with sleep specialists for diagnosis and follow-up.
Is genioplasty done with an implant?
I favour osseous genioplasty (your own bone) for precise, stable movement and natural contour; implants are reserved for specific indications.
Will I have visible scars?
Orthognathic and genioplasty incisions are inside the mouth. Parotid surgery uses discreet skin incisions planned along natural creases.
Can Botox fix clenching long-term?
Masseter modulation can ease tension and width, but bite mechanics and habits still matter. We combine it with splints, physio, and sleep strategies.